Understanding the Difference Between Medical Billing and Coding
Medical Billing and coding are the heart of healthcare payment. They make sure hospitals and doctors get paid for their care.
Many people think both jobs mean the same thing. But there is a clear difference between medical billing and coding. Both play unique parts in turning care into income. Together, they make records clean and claims move fast.
These two processes act as a bridge between doctors and insurers. They turn medical language into simple financial records. This helps keep hospitals running smoothly and without cash delays. When both jobs are done right, the full healthcare system works better.
What Is Medical Billing?
What Is Medical Coding?
Main Role
Medical coding changes doctor notes and tests into short codes.
These codes describe every disease, service, or care step clearly.
Purpose
It helps hospitals use one format for all patient records.
Insurers read these codes to decide on claim approval.
Process
Coders read doctor files and match codes to services.
They use ICD and CPT code lists to do this job.
Result
Clean coding makes Medical Billing faster and more accurate.
It also makes audits and care reviews easy and simple.
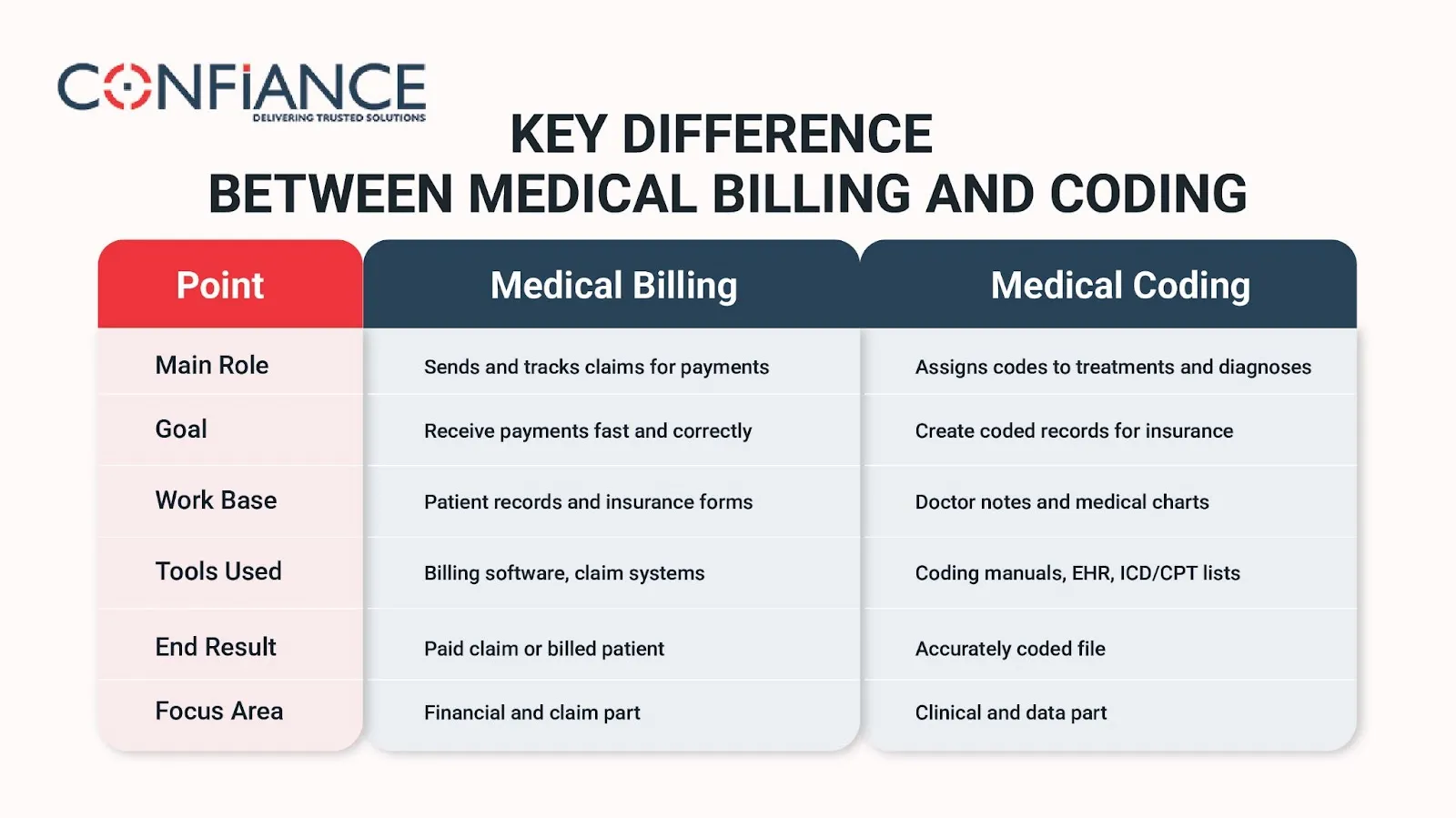
Key Difference Between Medical Billing and Coding
Let’s look at the difference between medical billing and coding step by step:
| Point | Medical Billing | Medical Coding |
|---|---|---|
| Main Role | Sends and tracks claims for payments | Assigns codes to treatments and diagnoses |
| Goal | Receive payments fast and correctly | Create coded records for insurance |
| Work Base | Patient records and insurance forms | Doctor notes and medical charts |
| Tools Used | Billing software, claim systems | Coding manuals, EHR, ICD/CPT lists |
| End Result | Paid claim or billed patient | Accurately coded file |
| Focus Area | Financial and claim part | Clinical and data part |
Why Both Are Needed Together
Steps in the Medical Billing Process
Steps in the Medical Coding Process
Step 1: Review Files
Coders check reports, notes, and care sheets from doctors.
They read each part and find all the care details needed.
Step 2: Pick Codes
They match care items with the right ICD or CPT codes.
Every service must have a correct and valid code.
Step 3: Enter Data
They type codes into digital health record systems daily.
This makes billing teams ready for the next claim creation.
Step 4: Check Quality
Coders review each file again before sharing with the billing staff.
It avoids wrong claims and wasted time fixing errors.
Step 5: Update Files
Old codes are replaced with new ones when rules change.
This keeps Medical Billing and coding current and compliant.
Skills Needed for Medical Billing
Skills Needed for Medical Coding
Medical Terms
Coders must know diseases, body parts, and test names.
This helps them choose the right code every time.
Focus
Each wrong code can cause loss or claim denial.
Coders must stay alert and recheck their work often.
Coding Tools
They use coding books, online systems, and EHR tools daily.
This keeps all patient records linked to Medical Billing data.
Privacy
They keep all patient info safe under HIPAA compliance rules.
This builds trust between hospitals and patients long-term.
Tools Used in Billing and Coding
Training and Certification
Common Workplaces
Hospitals
Hospitals hire large billing and coding teams for all claims.
They handle hundreds of patient files every single day.
Private Clinics
Small clinics use internal or outsourced Medical Billing support.
It saves time and lets doctors focus more on patient care.
Insurance Companies
Insurance firms need coders to review claim codes before approval.
They make sure all codes match the real care services given.
Outsourcing Firms
Many hospitals outsource billing and coding for fast claim cycles.
Still, the difference between medical billing and coding remains clear.
Benefits of Accurate Billing and Coding
Common Challenges
How Technology Helps
Career Scope
High Demand
Hospitals, clinics, and insurers need skilled coders and billers.
Job demand is rising as digital healthcare grows fast.
Income
Both jobs offer stable pay and room for long careers.
Certifications help increase pay scales and career trust.
Job Roles
Billers can become claim managers; coders can be auditors.
Many move into training, tech, or compliance after experience.
Future
The difference between medical billing and coding gives a career choice.
Both fields promise growth, learning, and good job stability.
Impact on Patients
Clear Bills
Patients get bills that match the care and treatment given.
This makes them trust clinics and doctors even more.
Fast Claims
Quick claims reduce stress and help patients save time.
Medical Billing ensures insurance payments come without big delays.
Fair Costs
Proper codes stop wrong or double charges from appearing.
Patients pay only what is real and approved by insurers.
Trust Factor
Clean systems make patients loyal to the same clinic longer.
Trust builds stronger healthcare relationships for years to come.
Link Between Billing, Coding, and Insurance
Tips for Accuracy
Stay Trained
Learn new code updates and insurance rules every few months.
Fresh skills keep work fast and reduce billing issues.
Good Communication
Coders and billers must talk to fix claim issues early.
Teamwork builds a strong and steady Medical Billing process.
Check Files
Double-check all data before sending out any claim form.
It saves time, money, and reputation for the hospital.
Follow Law
Keep data secure and follow all government billing standards.
This keeps both workers and clinics safe from legal trouble.
Future Trends
AI and Automation
AI tools will make billing and coding faster and cleaner.
Less manual work means more focus on patient care.
Remote Work
Many coders and billers already work from home today.
This trend will grow more with digital hospital systems.
Combined Jobs
The difference between medical billing and coding may soon merge.
New software lets one person manage both jobs easily.
Compliance Focus
Data safety and privacy will stay top priority for all.
Certified experts will lead future billing and coding work.
Medical Billing and coding form the base of healthcare finance. They turn doctor work into codes and then into payment. Knowing the difference between medical billing and coding saves time and errors. It builds better systems for both patients and healthcare teams.
Confiance provides reliable medical billing and coding services. Our certified experts handle claims, data, and payments with complete accuracy. We ensure hospitals receive faster payments and experience a smooth workflow. Confiance maintains precision, reduces errors, and keeps your process efficient. Partner with us to make your billing process seamless and stress-free.
FAQs
- What is Medical Billing?
It means creating and sending claims for payment approval. - What is medical coding?
It turns doctor records and care into short standard codes. - What is the main difference between medical billing and coding?
Billing manages payments; coding handles patient data and codes. - Why are both jobs needed?
They work together to get fast and correct payments. - Can one person do both jobs?
Yes, trained people can manage both tasks in small setups. - Is Medical Billing a good career?
Yes, it gives a stable income and high job demand. - Is coding harder than billing?
Coding needs more medical term study and rule updates. - How long does it take to learn?
Most people learn both within 6–12 months of study. - Do both use software?
Yes, both jobs rely on billing and coding software daily. - What happens if coding is wrong?
Claims get denied, and payments are delayed for weeks. - How often do codes change?
Codes update each year with new diseases and services. - Can errors cause legal issues?
Yes, wrong claims can lead to audits or penalties. - Who checks the claims before sending?
Billers check all claims and verify patient details first. - Why is data privacy important?
It keeps patient trust and meets legal health rules. - How does Medical Billing improve hospital cash flow?
It speeds up claim approvals and reduces pending payments. - What tools are used in billing?
Claim trackers, online forms, and accounting dashboards. - What tools are used in coding?
ICD, CPT lists, and hospital EHR software systems. - Can AI replace these jobs?
AI helps, but still needs humans for final reviews. - What is the link between coding and insurance?
Insurers read codes to approve or deny claims fast. - How do billers handle denied claims?
They correct issues and resend claims for approval. - What is the role of compliance in billing?
It ensures all bills follow national healthcare laws. - What happens if a bill is not submitted?
Hospitals lose income, and care providers face delays. - How is billing accuracy checked?
Audits and reports ensure claims are error-free before payment.
